How many neurons are in the brain? It’s a question that has puzzled scientists for centuries, and the answer is anything but simple. With an estimated 86 billion neurons in the average human brain, understanding their role in our thoughts, feelings, and actions is a daunting task.
Join us on a captivating journey into the depths of the human mind as we explore the mysteries of neuron count and its profound implications.
From the intricate connections that shape our memories to the electrical impulses that govern our movements, neurons are the building blocks of our very existence. In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of neuroscience, uncovering the latest research and unraveling the secrets of these remarkable cells.
The Importance of Neurons in the Brain
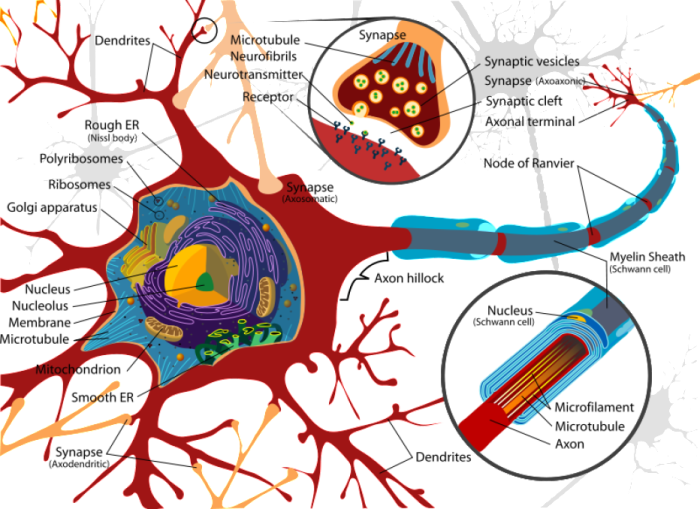
Neurons are the fundamental building blocks of the brain, responsible for processing, transmitting, and storing information. They play a vital role in our cognitive abilities, emotions, and physical functions.
Neurons communicate through electrical and chemical signals. Electrical signals, known as action potentials, travel along the neuron’s axon, while chemical signals, called neurotransmitters, are released at the synapse, the junction between two neurons.
Types of Neurons
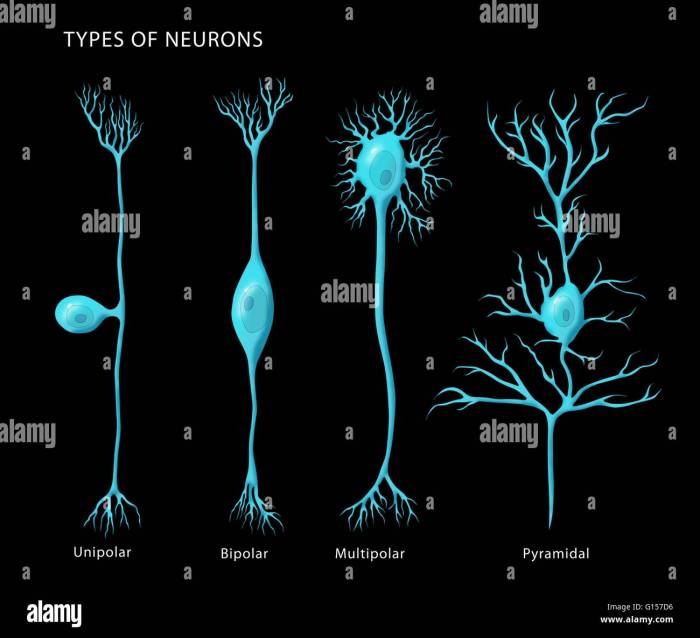
There are various types of neurons, each with a specific role in the brain:
- Sensory neuronsreceive information from the environment and transmit it to the brain.
- Motor neuronscarry signals from the brain to muscles, glands, and other organs.
- Interneuronsconnect different neurons within the brain, processing and integrating information.
Counting Neurons in the Brain: How Many Neurons Are In The Brain
Estimating the number of neurons in the brain is a complex and challenging task. The brain is a highly intricate organ, and its neurons are densely packed, making it difficult to count them accurately.
Historical Methods
Historically, scientists used various methods to estimate neuron count, including:
- Counting Stained Neurons:Researchers stained brain tissue with dyes that selectively bind to neurons. They then counted the stained neurons under a microscope.
- Cavalieri Principle:This method involves dividing the brain into thin slices and counting the neurons in each slice. The total neuron count is then estimated by multiplying the average neuron density by the brain’s volume.
Modern Techniques
Modern techniques for counting neurons include:
- Optical Clearing:This technique involves treating brain tissue with chemicals that make it transparent. Neurons can then be visualized and counted using high-resolution microscopy.
- Automated Image Analysis:Computer algorithms can be used to analyze images of brain tissue and identify and count neurons.
Estimated Number of Neurons in the Human Brain
The human brain is an incredibly complex organ, and one of the most important factors contributing to its complexity is the vast number of neurons it contains. Neurons are the fundamental units of the brain, and they are responsible for transmitting information throughout the brain and body.The exact number of neurons in the human brain is not known, but estimates range from 86 billion to 100 billion.
This wide range of estimates is due to the difficulty in accurately counting the number of neurons in the brain. Neurons are very small, and they are packed very densely together. This makes it difficult to count them accurately, even using advanced imaging techniques.The number of neurons in the brain varies from person to person.
Some people are born with more neurons than others, and some people lose neurons as they age. The number of neurons in the brain also varies depending on the region of the brain. Some regions of the brain, such as the cerebral cortex, have a very high density of neurons, while other regions, such as the brainstem, have a much lower density of neurons.
Comparative Analysis of Neuron Counts Across Species
The number of neurons in the brain varies significantly across species, ranging from a few thousand in simple organisms to trillions in complex animals. This variation is related to the size and complexity of the brain, which in turn is associated with cognitive abilities.
Relationship between Brain Size and Neuron Count
There is a general positive correlation between brain size and neuron count. Larger brains typically have more neurons, allowing for increased computational power and cognitive complexity. However, the relationship is not linear, and some species have larger brains relative to their neuron count than others.
This suggests that factors other than brain size also influence neuron count.
Implications for Cognitive Abilities
The number of neurons in the brain is thought to be a key factor in determining cognitive abilities. Species with more neurons generally have higher levels of intelligence, problem-solving skills, and memory capacity. However, the relationship between neuron count and cognitive abilities is complex, and other factors such as brain structure and connectivity also play a role.
Comparative Table of Neuron Counts
The following table compares neuron counts in the brains of different species:| Species | Neuron Count | Brain Weight (g) ||—|—|—|| Human | 86 billion | 1,300 || Chimpanzee | 78 billion | 400 || Dolphin | 40 billion | 1,500 || Elephant | 25 billion | 4,500 || Dog | 530 million | 75 || Cat | 250 million | 50 || Mouse | 75 million | 0.4 || Zebrafish | 100,000 | 0.005 |As the table shows, there is a wide range of neuron counts across species.
Humans have the highest neuron count, followed by chimpanzees, dolphins, and elephants. Dogs and cats have significantly fewer neurons, while mice and zebrafish have even lower counts.
Neuron Count and Brain Development
Neurogenesis is the process of generating new neurons. It occurs in the brain during development and in certain regions of the adult brain. During development, neurogenesis contributes to the increase in neuron count, which is essential for brain growth and function.
Environmental factors such as stress, nutrition, and social experiences can influence neurogenesis and neuron count.
Role of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in shaping neuron count during development. For example, exposure to stress can reduce neurogenesis and neuron count in the hippocampus, a brain region involved in learning and memory. Conversely, enriched environments that provide opportunities for exploration and learning can promote neurogenesis and increase neuron count.
Impact of Aging
Aging is associated with a decline in neuron count in certain brain regions. This decline is more pronounced in regions involved in higher-order cognitive functions, such as the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. The loss of neurons with age can contribute to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Emerging Research on Neuron Count
As neuroscience continues to advance, so do our techniques for counting neurons. Recent advancements in imaging and computational methods have enabled researchers to estimate neuron counts with greater accuracy and precision.
Ongoing Debates and Controversies
Despite these advancements, there are still ongoing debates and controversies surrounding neuron count estimates. One major area of debate is the accuracy of different counting methods. Some studies have suggested that certain methods may overestimate or underestimate the true number of neurons, leading to discrepancies in reported counts.
Areas for Future Research, How many neurons are in the brain
There are several areas where future research on neuron count is needed. One important area is the development of even more accurate and reliable counting methods. Another area of interest is the relationship between neuron count and brain function. Researchers are exploring how variations in neuron count may contribute to differences in cognitive abilities, behavior, and neurological disorders.
Epilogue
As we continue to unravel the complexities of the human brain, the question of how many neurons it contains remains a captivating enigma. While estimates vary, the sheer magnitude of this number underscores the incredible complexity and potential of the human mind.
Through ongoing research and technological advancements, we inch closer to understanding the intricate dance of neurons and their profound influence on our lives.
Essential FAQs
How many neurons are in the human brain?
Estimates range from 86 billion to over 100 trillion, with variations due to individual differences and counting methods.
Why is it difficult to count neurons accurately?
The sheer number of neurons, their intricate connections, and the limitations of imaging techniques pose challenges in obtaining precise counts.
How do neurons contribute to brain function?
Neurons transmit electrical and chemical signals, forming complex networks that process information, control movement, and govern our thoughts and emotions.






Leave a Comment