What can lacto vegetarians eat? Lacto vegetarians, a subset of vegetarians, follow a diet that excludes meat, poultry, fish, and eggs but allows dairy products. This unique dietary approach offers a range of potential health benefits and presents a distinct set of considerations for meal planning.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of lacto vegetarianism, exploring its definition, benefits, food sources, and more.
Lacto vegetarianism offers a flexible and balanced approach to plant-based eating, providing essential nutrients while allowing for the inclusion of dairy products. Understanding the dietary guidelines and exploring the diverse food options available to lacto vegetarians empowers individuals to make informed choices and reap the rewards of this unique dietary approach.
Definition of Lacto Vegetarianism
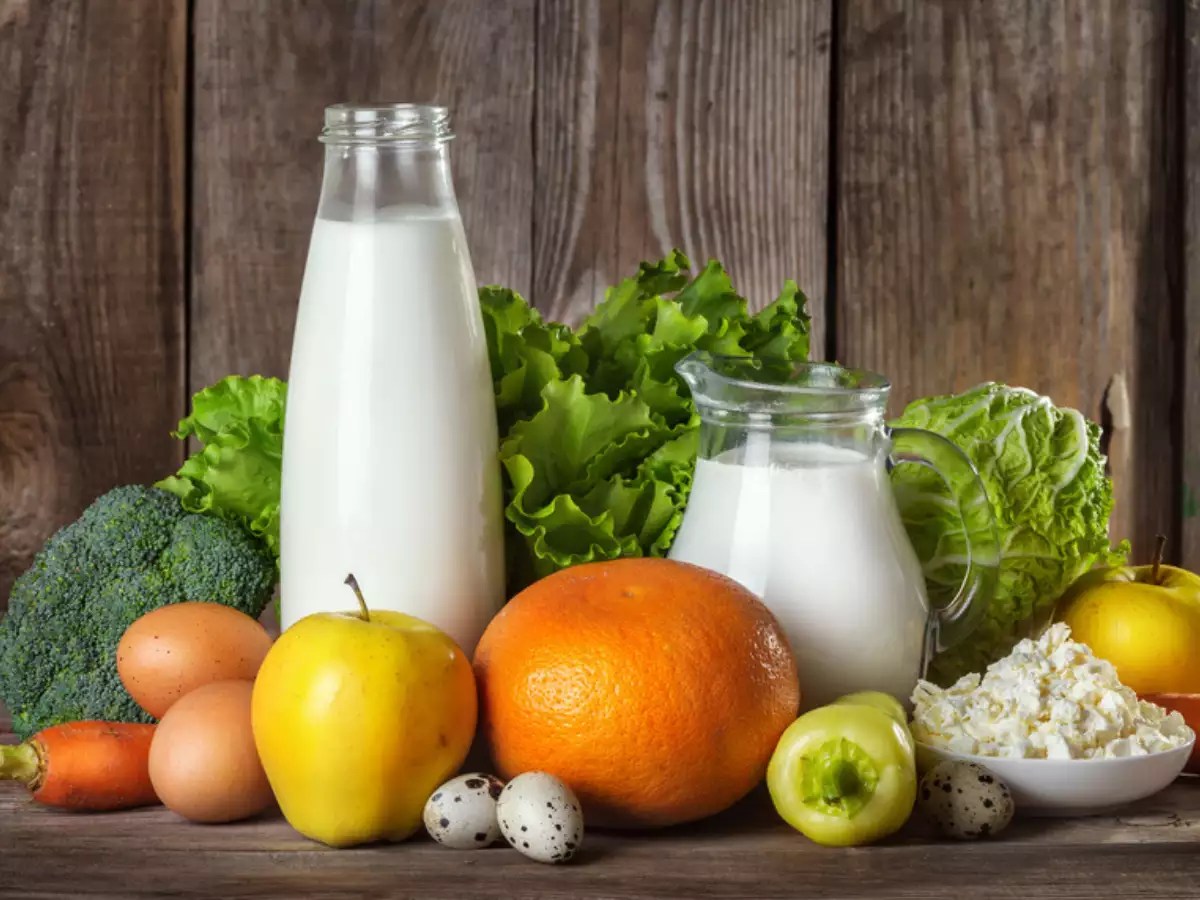

Lacto vegetarianism is a type of vegetarian diet that includes dairy products but excludes all other animal-derived foods.
Lacto vegetarians choose to consume dairy products because they provide essential nutrients, such as calcium, protein, and vitamin B12. Common dairy products consumed by lacto vegetarians include milk, yogurt, cheese, and butter.
Inclusion of Dairy Products
Dairy products are an important part of the lacto vegetarian diet. They provide essential nutrients that are not easily obtained from plant-based sources.
- Calcium:Dairy products are a rich source of calcium, which is essential for bone health.
- Protein:Dairy products are also a good source of protein, which is essential for building and repairing tissues.
- Vitamin B12:Vitamin B12 is a nutrient that is not found in plant-based foods. Dairy products are a good source of vitamin B12, which is essential for red blood cell production.
Benefits of a Lacto Vegetarian Diet: What Can Lacto Vegetarians Eat
Adopting a lacto vegetarian diet can offer numerous health benefits. By incorporating dairy products into their diet, lacto vegetarians can reap the benefits of essential nutrients like calcium, protein, and vitamins.
Role of Dairy Products
Dairy products, such as milk, yogurt, and cheese, are rich sources of calcium, a mineral crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth. They also provide protein, essential for building and repairing tissues, and a range of vitamins, including vitamin D, B12, and riboflavin.
Importance of Calcium
Calcium is a vital nutrient for maintaining bone health. A lacto vegetarian diet provides a good source of calcium through dairy products. Adequate calcium intake helps prevent osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones.
Importance of Protein
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues. Dairy products are a good source of high-quality protein, containing all the essential amino acids the body needs. Protein from dairy products can help maintain muscle mass and support overall growth and development.
Importance of Vitamins
Dairy products are also a good source of several vitamins, including vitamin D, B12, and riboflavin. Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, while vitamin B12 is crucial for nerve function and red blood cell production. Riboflavin is important for energy production and cell growth.
Food Sources for Lacto Vegetarians
Lacto vegetarians adhere to a plant-based diet that incorporates dairy products. This dietary choice provides a wide array of nutrient-rich food sources, ensuring a balanced and healthy lifestyle.
Lacto vegetarians can enjoy a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These plant-based foods are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants.
If you’re a pescatarian, you might be wondering if eating fish is considered vegetarian. The answer is a bit complicated, as there are different definitions of vegetarianism. Some people define vegetarians as those who don’t eat any meat, including fish, while others define vegetarians as those who don’t eat any land animals, but do eat fish and other seafood.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not eating fish is considered vegetarian is up to you. If you’re not sure, you can always consult with a registered dietitian or other healthcare professional to get their opinion. is eating fish considered vegetarian
Fruits
- Apples
- Bananas
- Berries (blueberries, raspberries, strawberries)
- Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits, lemons)
- Mangoes
- Pears
- Pineapples
Vegetables
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Carrots
- Celery
- Cucumbers
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, collard greens)
- Mushrooms
- Onions
- Potatoes
- Sweet potatoes
- Tomatoes
Legumes
- Beans (black beans, kidney beans, pinto beans)
- Chickpeas
- Lentils
- Peas
Nuts and Seeds
- Almonds
- Cashews
- Chia seeds
- Flax seeds
- Peanuts
- Pumpkin seeds
- Sunflower seeds
- Walnuts
Dairy Products
Lacto vegetarians incorporate dairy products into their diet, providing a valuable source of calcium, protein, and other essential nutrients.
- Milk:Rich in calcium, vitamin D, and protein.
- Yogurt:Provides calcium, protein, probiotics, and vitamin B12.
- Cheese:Contains calcium, protein, and healthy fats.
- Cottage cheese:High in protein and calcium.
- Sour cream:Provides calcium and healthy fats.
Meal Planning for Lacto Vegetarians
Meal planning for a lacto vegetarian diet can be easy and nutritious. Here’s a sample meal plan to get you started:
Breakfast
* Oatmeal with berries, nuts, and milk (1 cup cooked oatmeal, 1/2 cup berries, 1/4 cup nuts, 1 cup milk)
While the question of “is eating fish considered vegetarian” may seem like a straightforward one, the answer is not as clear-cut as you might think. For those who follow a vegetarian diet, the definition of what constitutes as vegetarian food can vary widely.
Some vegetarians choose to abstain from all animal products, including fish, while others may include fish in their diet. Is eating fish considered vegetarian ? The answer depends on your individual definition of vegetarianism.
- Yogurt parfait with granola and fruit (1 cup yogurt, 1/2 cup granola, 1/2 cup fruit)
- Whole-wheat toast with avocado and eggs (2 slices toast, 1/2 avocado, 2 eggs)
Lunch, What can lacto vegetarians eat
* Salad with grilled tofu, vegetables, and quinoa (1 cup salad greens, 1/2 cup grilled tofu, 1 cup vegetables, 1/2 cup cooked quinoa)
- Lentil soup with whole-wheat bread (1 bowl lentil soup, 2 slices whole-wheat bread)
- Veggie burger on a whole-wheat bun with lettuce, tomato, and onion (1 veggie burger, 1 whole-wheat bun, lettuce, tomato, onion)
Dinner
* Vegetarian chili with cornbread (1 bowl vegetarian chili, 1 piece cornbread)
- Pasta with marinara sauce and vegetables (1 cup pasta, 1/2 cup marinara sauce, 1 cup vegetables)
- Shepherd’s pie with lentils and mashed potatoes (1 serving shepherd’s pie)
Snacks
* Fruit (apple, banana, orange)
- Vegetables (carrots, celery, cucumber)
- Yogurt (1 cup)
- Trail mix (1/4 cup nuts, 1/4 cup seeds, 1/4 cup dried fruit)
Challenges and Considerations
Adopting a lacto vegetarian diet presents certain challenges that require careful attention.
One significant concern is ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients, particularly those commonly found in animal products. These include protein, iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Meeting Nutritional Needs
To meet these nutritional needs through plant-based sources, lacto vegetarians should focus on consuming:
- Protein:Beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, and seeds
- Iron:Leafy green vegetables, fortified cereals, and beans
- Calcium:Dairy products, fortified plant-based milks, and leafy green vegetables
- Vitamin B12:Fortified plant-based foods or supplements
- Omega-3 fatty acids:Fatty fish, flaxseed, and walnuts
Comparison to Other Vegetarian Diets
Lacto vegetarianism falls under the umbrella of vegetarian diets, which exclude meat, poultry, fish, and seafood. However, it differs from other vegetarian diets in terms of its dietary restrictions and nutritional implications.
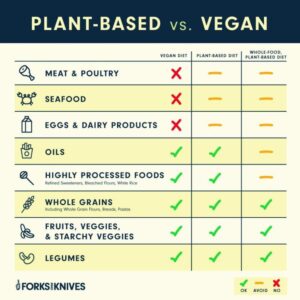
Lacto Vegetarianism vs. Veganism
Veganism is the most restrictive form of vegetarianism, excluding all animal products, including dairy, eggs, and honey. In contrast, lacto vegetarians consume dairy products, which provide essential nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and protein.
Lacto Vegetarianism vs. Ovo-Vegetarianism
Ovo-vegetarians exclude meat, poultry, fish, seafood, and dairy products but allow eggs in their diet. Eggs are a good source of protein, iron, and vitamins A, D, and E. Compared to lacto vegetarians, ovo-vegetarians may have a lower intake of calcium and vitamin D.
Nutritional Implications
All vegetarian diets, including lacto vegetarianism, provide numerous health benefits, such as reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer. However, each diet has its own nutritional considerations:
- Lacto vegetarians have a higher risk of vitamin B12 deficiency, which can be obtained from animal products.
- Vegans have a higher risk of calcium and vitamin D deficiency, which can be obtained from dairy products and eggs.
- Ovo-vegetarians have a higher risk of iron deficiency, which can be obtained from meat and eggs.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, lacto vegetarianism presents a balanced and nutritious dietary approach that allows for the inclusion of dairy products. By embracing a wide variety of plant-based foods and incorporating dairy sources, lacto vegetarians can enjoy a fulfilling and healthful lifestyle.
Whether seeking to improve overall well-being, reduce environmental impact, or simply explore new culinary horizons, lacto vegetarianism offers a rewarding and sustainable path.
Helpful Answers
What is the primary difference between lacto vegetarians and vegans?
Lacto vegetarians consume dairy products, while vegans exclude all animal products, including dairy, eggs, honey, and gelatin.
Can lacto vegetarians get enough protein?
Yes, lacto vegetarians can obtain adequate protein from plant-based sources such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, as well as from dairy products.
What are some challenges faced by lacto vegetarians?
Ensuring adequate intake of vitamin B12, which is primarily found in animal products, can be a challenge for lacto vegetarians. Fortified foods or supplements may be necessary.



Leave a Comment