Embark on a culinary adventure as we delve into the world of eating only fish and vegetables. From nutritional benefits to environmental impact, this comprehensive guide will unveil the intricacies of this unique dietary choice.
Prepare to be captivated by the fascinating insights and practical advice that await you within these pages.
Nutritional Considerations
Adopting a diet centered around fish and vegetables offers a myriad of nutritional benefits. Fish, especially fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel, are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart health, brain function, and inflammation reduction.
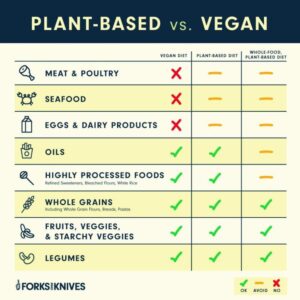
Embarking on a vegan diet can seem daunting, but it doesn’t have to be. What can I eat on a vegan diet ? The answer is plenty! Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds are all staples of a vegan diet, providing a wide array of nutrients and flavors to keep you satisfied.
Vegetables, on the other hand, provide an array of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, which are crucial for overall well-being.
However, it’s important to note that a diet restricted solely to fish and vegetables may pose certain nutritional deficiencies. One primary concern is the lack of vitamin B12, which is primarily found in animal products. Vitamin B12 is essential for red blood cell formation, nerve function, and DNA synthesis.
Another potential deficiency is vitamin D, which is crucial for bone health and immune function. While some fish, such as salmon and tuna, contain vitamin D, it may not be sufficient to meet daily requirements.
Ensuring Adequate Nutrient Intake
To ensure adequate nutrient intake while following a fish and vegetable-based diet, it’s essential to include fortified foods or supplements. Fortified plant-based milk, cereals, and nutritional yeast can provide vitamin B12. Additionally, regular exposure to sunlight can help the body produce vitamin D, or supplementation may be necessary, especially during winter months.
Furthermore, it’s important to consume a variety of vegetables to obtain a wide range of nutrients. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and kale are excellent sources of antioxidants and fiber. Leafy greens like spinach and kale are rich in vitamins A, C, and K.
Legumes, such as beans and lentils, provide protein, fiber, and iron.
By incorporating these recommendations, individuals can enjoy the nutritional benefits of a fish and vegetable-based diet while minimizing the risk of nutrient deficiencies.
Health Implications
Adopting a diet centered around fish and vegetables offers numerous health benefits. Studies have consistently shown that individuals who consume these foods regularly experience a reduced risk of chronic diseases, improved cognitive function, and enhanced overall well-being.
Nutritional Value
- Fish and vegetables are nutrient-dense, providing a wide range of essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber.
- Fish is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are crucial for heart and brain health.
- Vegetables provide an abundance of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as folate, potassium, and fiber.
Potential Health Risks
While a diet rich in fish and vegetables is generally considered safe, there are a few potential health risks to consider:
- Mercury Exposure:Some types of fish, such as tuna and swordfish, may contain elevated levels of mercury. Consuming large amounts of these fish can lead to mercury toxicity, which can affect the nervous system and kidneys.
- Nutrient Deficiencies:A diet that excludes all other food groups may lead to deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as vitamin B12, iron, and calcium.
Long-Term Effects, Eating only fish and vegetables
The long-term effects of consuming only fish and vegetables are not fully understood. However, studies have shown that people who follow this dietary pattern tend to have lower rates of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
It’s important to note that a diet consisting solely of fish and vegetables may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain health conditions or dietary restrictions may need to adjust their intake or consult with a healthcare professional.
Environmental Impact
Choosing a diet centered around fish and vegetables can have significant implications for the environment. Understanding these impacts is crucial for making informed dietary choices.
Compared to diets heavy in animal products, a fish-and-vegetable-based diet generally has a lower environmental footprint. Animal agriculture, particularly the production of red meat, is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, water pollution, and deforestation.
Sustainable Seafood Practices
When consuming fish, it’s essential to consider sustainable seafood practices. Overfishing, bycatch, and habitat destruction pose significant threats to marine ecosystems. Choosing fish from well-managed fisheries certified by organizations like the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) helps support sustainable practices and reduce environmental impact.
By incorporating these considerations into dietary choices, individuals can contribute to preserving marine ecosystems and mitigating the environmental impact of their food consumption.
Culinary Considerations
Adopting a diet consisting solely of fish and vegetables requires careful planning to ensure nutritional adequacy and culinary satisfaction. This section provides a sample meal plan, nutritional composition of key meals, and tips for preparing and cooking these foods in a healthy and flavorful way.
Sample Meal Plan
A sample meal plan for a day might include:
- Breakfast:Oatmeal with berries and nuts
- Lunch:Grilled salmon with roasted vegetables
- Dinner:Lentil soup with a side of steamed broccoli
- Snacks:Apple with peanut butter, carrot sticks with hummus
Nutritional Composition
The nutritional composition of key meals from the sample meal plan is Artikeld in the following table:
| Meal | Calories | Protein (g) | Carbohydrates (g) | Fat (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grilled salmon with roasted vegetables | 400 | 30 | 30 | 15 |
| Lentil soup with steamed broccoli | 350 | 20 | 40 | 10 |
Tips for Preparing and Cooking
Here are some tips for preparing and cooking fish and vegetables in a healthy and flavorful way:
- Choose fresh, high-quality ingredients.This will ensure the best flavor and nutritional value.
- Cook fish simply.Grilling, baking, or steaming are all healthy cooking methods that preserve the delicate flavor of fish.
- Roast vegetables.Roasting vegetables brings out their natural sweetness and intensifies their flavor.
- Use herbs and spices.Herbs and spices can add flavor and complexity to both fish and vegetables.
- Don’t overcook.Overcooking can toughen fish and make vegetables mushy.
Final Review: Eating Only Fish And Vegetables
As we conclude our exploration of eating only fish and vegetables, it becomes evident that this dietary pattern offers a myriad of health benefits, environmental advantages, and culinary delights. However, it also requires careful planning and consideration to ensure adequate nutrient intake and address potential concerns.
Whether you’re a seasoned pescatarian or simply curious about the possibilities, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge and inspiration to make informed choices about your dietary journey.
FAQ Corner
Is eating only fish and vegetables healthy?
Yes, a diet rich in fish and vegetables can provide numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer.
What are the potential nutritional deficiencies associated with eating only fish and vegetables?
Vitamin B12, iron, and calcium are nutrients that may be deficient in a diet consisting solely of fish and vegetables. Supplementation or fortified foods may be necessary to prevent deficiencies.
How can I ensure I’m getting enough protein on a fish and vegetable diet?
Fish is an excellent source of protein. Aim to consume at least 3-4 servings of fish per week to meet your protein needs.
Is eating only fish and vegetables sustainable?
The sustainability of a fish and vegetable diet depends on the types of fish consumed and the fishing practices used. Choose sustainable seafood options and support fisheries that prioritize environmental conservation.



Leave a Comment